RsyncUI provides default parameters for data synchronization. However, the actual default parameters utilized in tasks are determined by whether the rsync operation is performed over a network connection or to a local attached disk.
User Parameter Management
Users have the ability to modify default parameters as necessary. Parameters to rsync are stored in tasks, including a local ssh parameter. The local ssh parameter overrides a global ssh parameter if set.
SSH Key Handling
If default ssh-key values are employed and no information regarding ssh-keys is provided in RsyncUI, the parameter -e ssh is
appended to the rsync command to ensure data is tunneled and encrypted using ssh. This applies exclusively to remote servers and data restoration.
Task-Specific SSH Parameters
Task-specific ssh parameters override global ssh parameters configured in the user settings.
- ssh port: Specify if ssh utilizes a port other than the standard port 22.
- ssh-keypath and identity file: Typically, these are
.ssh/id_rsa. Set only if alternative keypath and identity file are to be utilized by ssh.
Adding Parameters to Rsync
To add a parameter to rsync, enter it in the corresponding field. RsyncUI supports seven user-defined parameters. Users can add parameters using any of the fields. However, users are responsible for verifying the accuracy of the added parameters. If an incorrect parameter is added, rsync will generate an error message.
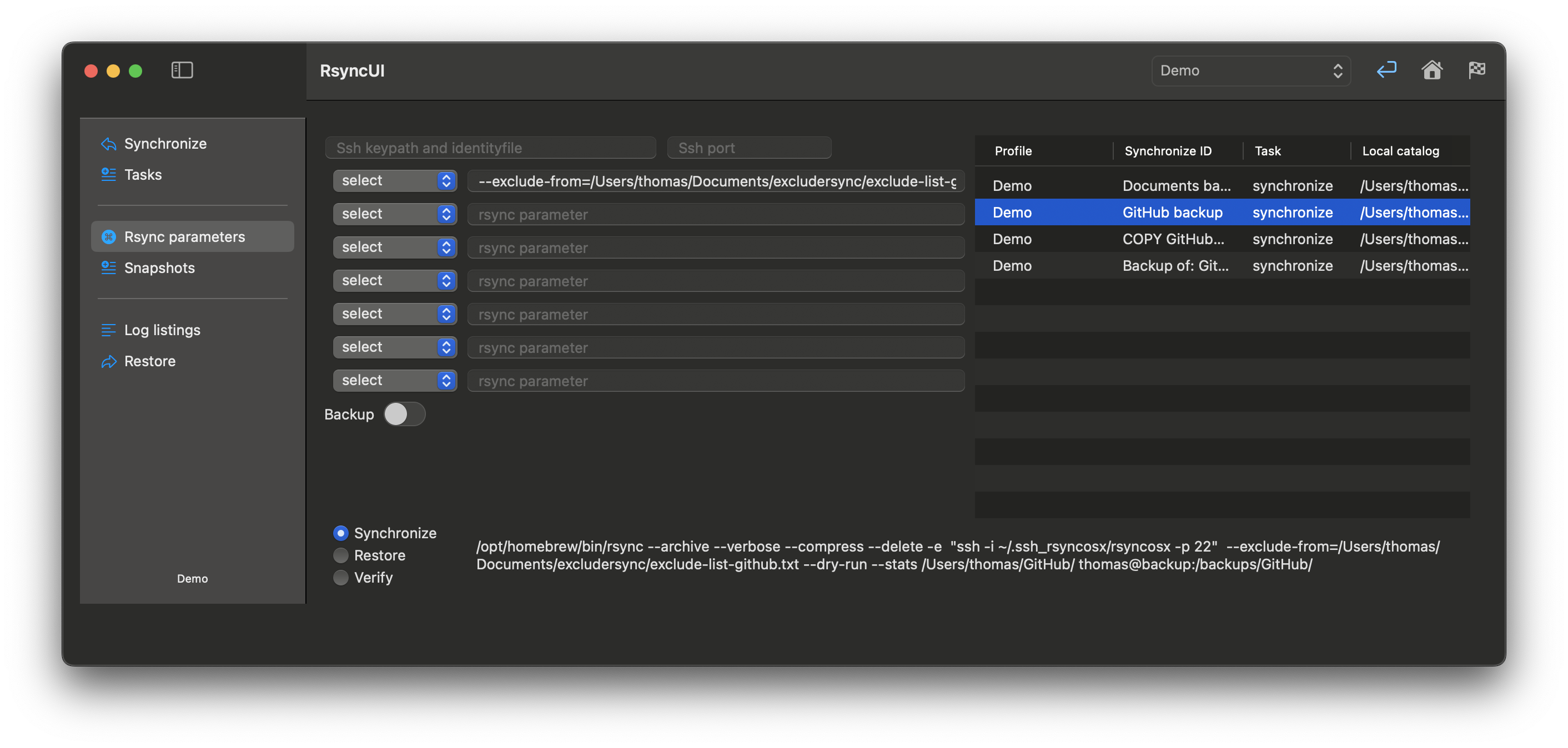
Parameters
Parameters are typically constructed as follows:
- parameter=value
--exclude-from=/Volumes/home/user/exclude-list.txt
--stats: Enables the display of statistics during the synchronization process.--dry-run: Executes a simulated synchronization without modifying the files.
For a comprehensive list of parameters for rsync, please refer to the rsync documentation.
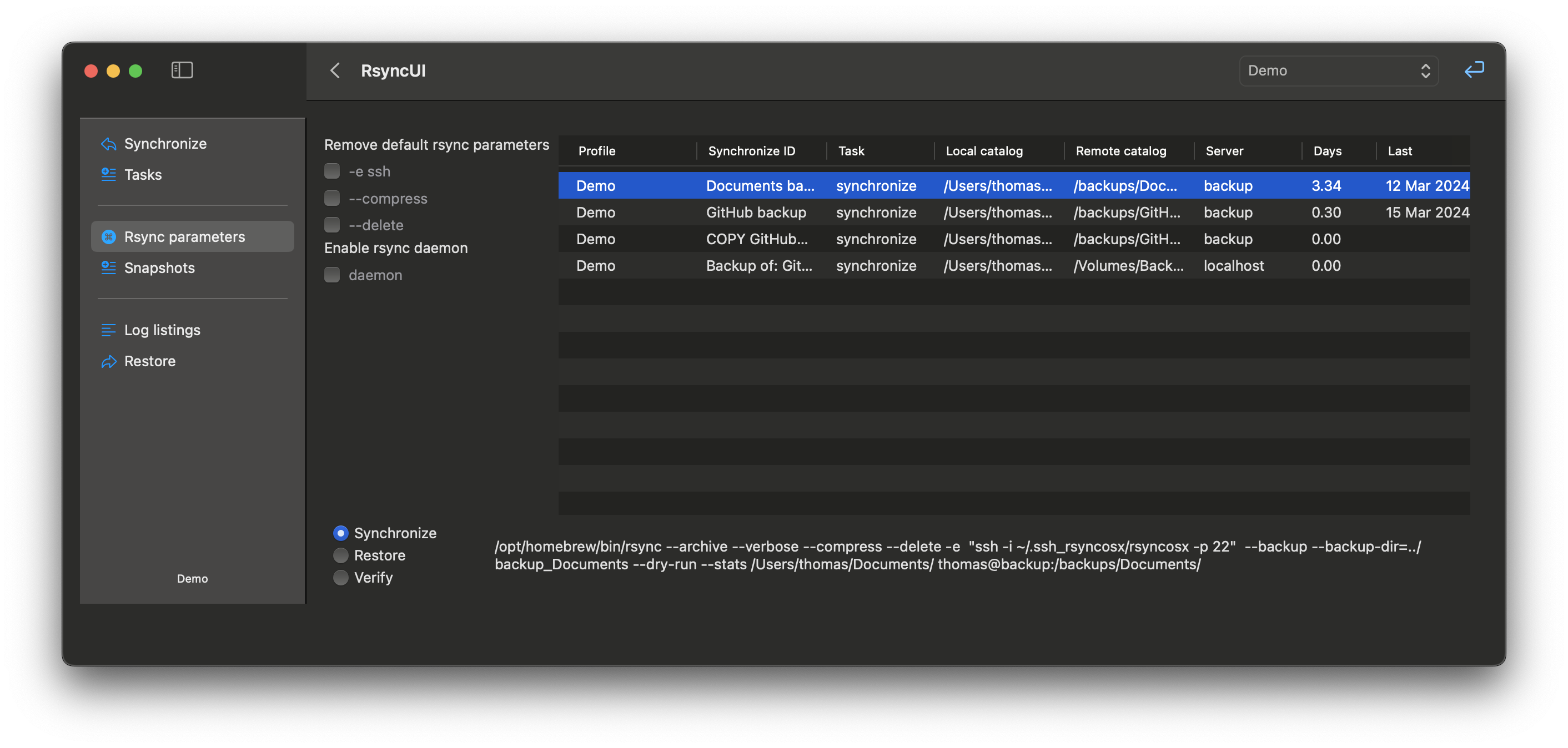
Backup Switch
The rsync command allows you to instruct it to save modified and deleted files in a separate backup catalog prior to the synchronization process.
This feature can be enabled by setting the following parameters:
--backup: Enables the saving of modified files.--backup-dir: Specifies the directory where modified or deleted files should be saved before synchronization. TheRsyncUIprovides a default value for this parameter, but you can customize it as per your requirements.
The default backup catalog for the <catalog to synchronize> relative to the synchronized catalog is ../backup_<catalog to synchronize>.
Verify Changes
The resulting command-line string is dynamically updated when modifying parameters. The Play icon on the toolbar allows you to test new parameters
before saving them. The Play executes a --dry-run task for verification of parameters.
The Play icon is context-sensitive. If the verify switch is selected, the Verify command is executed.
Similarly, the synchronize and restore switches execute the corresponding commands.